Digital Video Recorder (DVR) and Network Video Recorder (NVR) systems are essential components of modern surveillance and security setups, providing users with the ability to record, store, and manage video footage from security cameras. While both systems serve similar purposes, they differ in their underlying technology and functionality. In this guide, we’ll delve into how DVR and NVR systems work, their key features, and their respective advantages.
1. DVR System Overview:
DVR systems are designed to record and store video footage from analog security cameras. These systems typically consist of a DVR unit, analog cameras, and a storage device, such as a hard drive. The DVR unit processes the video signals received from the analog cameras, converts them into digital format, and compresses the footage for efficient storage. Users can then access the recorded footage through the DVR’s user interface or remotely via a network connection.
2. NVR System Overview:
In contrast, NVR systems are designed to work with IP (Internet Protocol) cameras, which capture and transmit video footage over a network connection. NVR systems consist of an NVR unit, IP cameras, and a storage device. The NVR unit receives the video streams from the IP cameras over the network, processes the footage, and stores it on the connected storage device. NVR systems offer advanced features such as remote access, motion detection, and intelligent video analytics.
3. How DVR Systems Work:
DVR systems utilize analog cameras, which capture video footage in analog format. The DVR unit receives the analog video signals from the cameras, digitizes them using an analog-to-digital converter, and compresses the footage using video codecs such as H.264 or H.265. The compressed video data is then stored on the DVR’s internal hard drive or external storage device. Users can view live or recorded footage through the DVR’s interface or remotely via a network connection.
4. How NVR Systems Work:
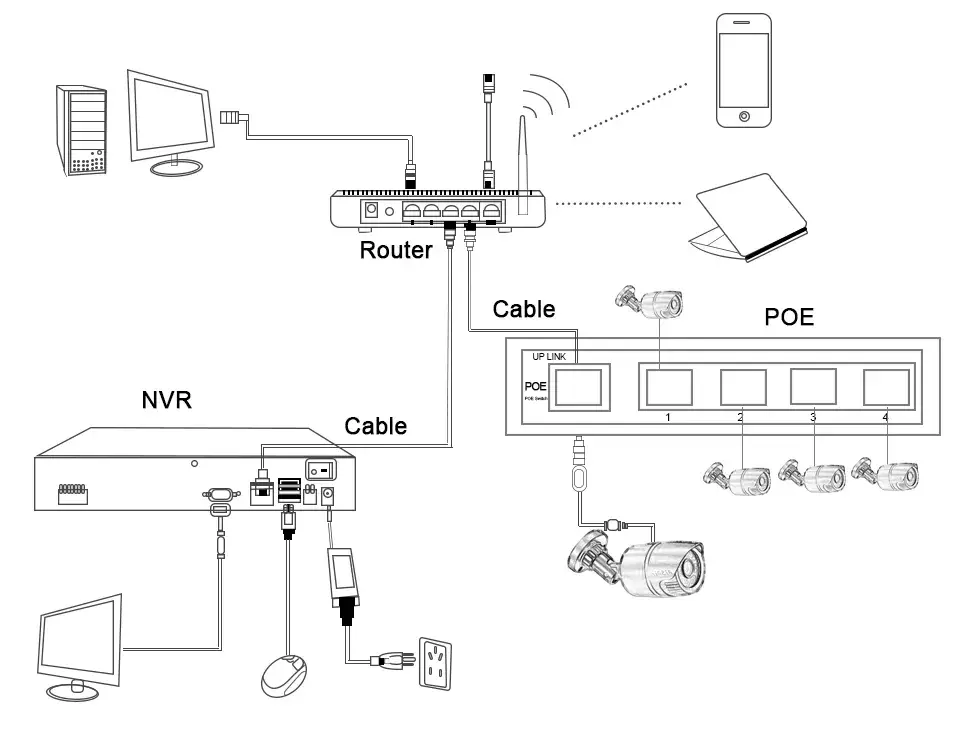
NVR systems work with IP cameras, which capture and transmit digital video footage over an IP network. The NVR unit receives the video streams from the IP cameras, decodes the footage, and stores it on the connected storage device. NVR systems can handle high-resolution video streams and offer advanced features such as remote access, real-time monitoring, and motion detection. Users can access live or recorded footage from anywhere with an internet connection using a computer or mobile device.
5. Key Features and Advantages:
Both DVR and NVR systems offer various features and advantages:
- Remote Access: Users can view live or recorded footage remotely from anywhere with an internet connection, enhancing monitoring capabilities and flexibility.
- Motion Detection: Both systems support motion detection functionality, allowing users to receive alerts and notifications when motion is detected in the camera’s field of view.
- Scalability: NVR systems offer greater scalability than DVR systems, as they can support a larger number of IP cameras and offer more flexible deployment options.
- Video Analytics: NVR systems often include advanced video analytics features, such as facial recognition, object detection, and people counting, providing enhanced security and surveillance capabilities.
- Compatibility: DVR systems are compatible with analog cameras, while NVR systems are designed for use with IP cameras, offering users flexibility in choosing their preferred camera technology.
In conclusion, DVR and NVR systems play critical roles in modern surveillance and security setups, offering users the ability to record, store, and manage video footage from security cameras. By understanding how these systems work and their key features, users can make informed decisions when selecting the right solution for their specific security needs.